The Power Of Visions
From FORwiki
| Project Visions and Visioning | |
|---|---|
| | This article is developed within the scope of the Project Visions and Visioning, an effort to enhance Foresight learning through collaborative work. |
The Power of Visions is the first lecture from a module on Visions and Visioning, first taught to graduate students from the Communication Faculty of the National School for Political and Administration Studies (Romania).
Contents |
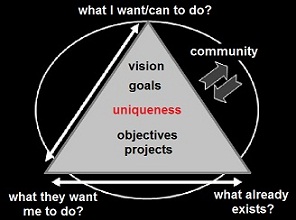
Why do we need to know about visions?
Is there a connection between having a shared vision and having good projects?
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Every project must be based on ...
- trust
- a real need
- measurable objectives
- uniqueness
The Organizational Kit
- one page on your vision and the problem to be solved
- one page about the organization
- one page per project:
- ¼ page about the specific problem/ subject
- ¼ page about what has been done so far and the uniqueness of the project
- ¼ page about the program
- ¼ page about the budget (main lines)
Additional elements
- full budgets and “shopping lists”
- articles about the projects/ the problems
- pictures about the projects/ the problems
- official documents
- appreciation letters
The Case Statement
- represents your ”signature”
- short presentation (150 words)
- identifies the need
- expresses a vision
- what are you all about
- justification of uniqueness
Example
More than 10 percent of the population in our country suffers from hearing loss. Every third person above the age of 65 is hard of hearing. Hearing loss affects all levels of society and causes difficulties in socialization and communication. The obstacles to coping with hearing loss include shame and denial. Hearing loss interferes with one’s ability to communicate with the surrounding environment, thus disturbing all aspects of life.
B. is the only organization founded and managed by people who are hard of hearing. The organization works actively to improve and advance the quality of life of hard of hearing people ages 18 and above. Our work includes lobbying for laws to improve accessibility, promoting the rights of the hard of hearing, removing the barrier of shame surrounding hearing loss, and encouraging and providing tools for the hard of hearing to cope with hearing loss.
How are shared visions being built?
The Foresight Exercise
Main article: Introduction to Foresight
Foresight is a systematic, participatory, future-intelligence-gathering and medium-to-long-term vision-building process aimed at present-day decisions and mobilizing joint actions.
Doing Foresight
Main article: Participatory nature of Foresight
- decision support – the goal is to identify needs and to produce knowledge that can be used during decision-making processes
- participatory nature – representatives of a diversity of societal groups are to be consulted during the foresighting process
- analyses alternative futures – the assumption is that the future is not pre-determined, but can evolve in different directions, according to decisions the decisions that are being made by actors
Characteristics
Main article: Communicating Foresight results
- systematic process of understanding challenges that might be bestowed upon us by the future, and identifying desirable states-of-affaires that can be reached through actions that may (or may not) be implemented today
- participatory and multidisciplinary process, which assumes the involvement of a diverse expertise belonging to different societal groups of actors
Why take a spare wheel?
The governance agent becomes the central actor
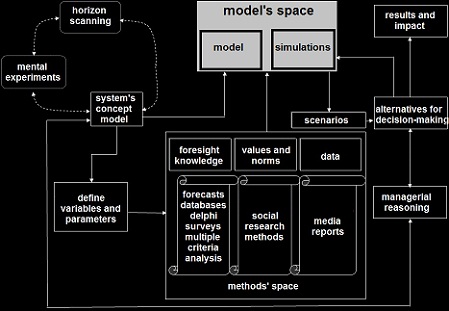
A general model for foresight exercises
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Foresight projects or Foresight activities?
How is vision building contributing to strategic planning?
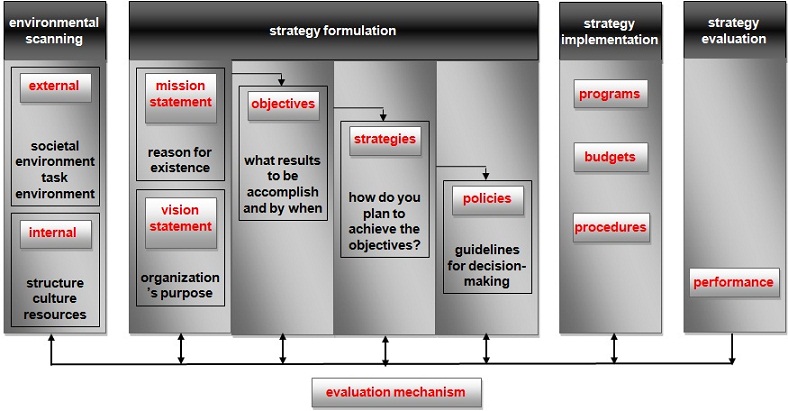
Strategic Management Model
Main article: Strategy Formulation
Mission and Vision Statement
The mission statement describes the role of a socio-economic sector in the society; the philosophy of how an organization is functioning.
The vision statement describes a unique purpose; how the sector/organization or the world is desirable to become.
Objectives
- the end-result of a planned activity
- the state of what is to be accomplished and by when
- should be quantified if possible
- achieving the objectives should result in the fulfillment of the vision
- the goal is an open-ended statement of what is to be accomplished with no quantification
Strategies
- comprehensive master plan stating how the objectives are to be achieved
- for strategic units
- corporate strategy – attitude towards growth: stability, growth, retrenchment
- business strategy - attitude towards other actors: competition or cooperation
- functional strategy – attitude towards a functional area of operations (for instance, technology followers or technology leaders)
- hierarchy of strategies
Policies
- broad guidelines for decision-making that link formulation of strategy with implementation
- used to make sure that all the people inan organization make decisions and take actions that support vision, objectives, and strategies
- example: a ”no questions asked” return policy
Modes of Strategic Decision-Making
- involve a change of major kind
- long-term in their impact
- they affect and shape the direction a whole socio-economic sector
- they are made by senior decision-makers
- deal with harmonizing organizational capabilities with the threats and opportunities
Planned Mode
- based on systematic gathering of information for situation analysis
- involves attempted rational selection of appropriate strategy
- pro-active search of opportunities and reactive reactions to existing problems
Entrepreneurial Mode
- the strategy is made by one powerful individual (i.e, the founder of a corporation), and relies on his personal vision of directions that are to be followed
- focus on opportunities, ignore problems
- large, bold decisions
- Ford Motor Company
Adaptive Mode
- reactive solutions to existing problems, rather pro-active research of opportunities
- a lot of negociating effort regarding priorities
- fragmented strategy, incremental development
- typical for universities
Logical Incrementalism
- synthesis of planning and adaptive decision-making
- top management has a lear idea about vision and objectives
- strategy is an interactive process, in which future is probed and organizational learning occurs
- strategy emerges through dialog and experiment
The Future of Communication
- Future of Communication
- Future Communication Networks
- What's the Future for Advertising?
- Future of Advertising Agencies
- Shifting values and the Future of Advertising
Pedagogical Features
Media:Curs 1 - the power of visions en.pdf - original slides from the first presentation of this lecture